RunwayJob
This type of workload deploys a Cloud Run Job. Jobs can be triggered on a schedule and/or on-demand (manually triggered CI job).
You can only define a single job per Runway workload. If you need to define multiple jobs, you will have to create a new Runway service in the provisioner for every job.
Example
Section titled “Example”apiVersion: runway/v1kind: RunwayJobmetadata: owner_email_handle: ... department: ... department_group: ... product_category: ...spec: region: us-central1 command: - /path/to/command args: - arg1 - arg2 schedule: cron: "1 6,14,22 * * *"Unlike services (which can be deployed to multiple
regions), jobs can only be deployed and executed in a single region (default: us-east1).
Refer to the schema for all supported configuration options.
Schedule
Section titled “Schedule”To configure a job to run on a schedule, simple set the spec.schedule.cron
attribute to any valid
crontab compatible
string as shown in the example above.
To pause a cronjob, simply set spec.schedule.paused to true:
apiVersion: runway/v1kind: RunwayJobmetadata: ...spec: ... schedule: cron: "1 6,14,22 * * *" paused: trueOn-demand
Section titled “On-demand”To have the ability to trigger a job on-demand, you will need to add a job to
your .gitlab-ci.yml similar to the following:
include: - project: 'gitlab-com/gl-infra/platform/runway/runwayctl' file: 'ci-tasks/service-project/runway.yml' inputs: runway_service_id: example-job-431wm0 image: "$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/example-service:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA}" runway_version: v3.40.0
Trigger Example Job - staging: extends: .[example-job-431wm0] Execute Job staging
Trigger Example Job - production: extends: .[example-job-431wm0] Execute Job productionReplace example-job-431wm0 with your Runway service ID for your desired job.
You will see two new jobs appear in your pipelines:
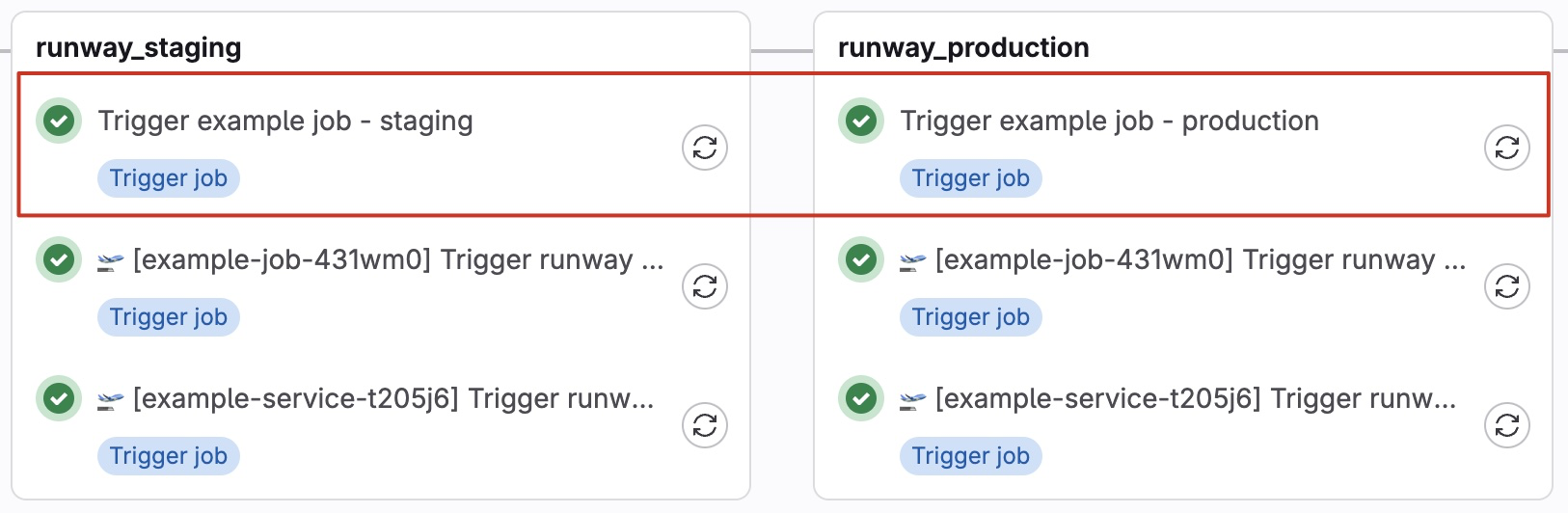
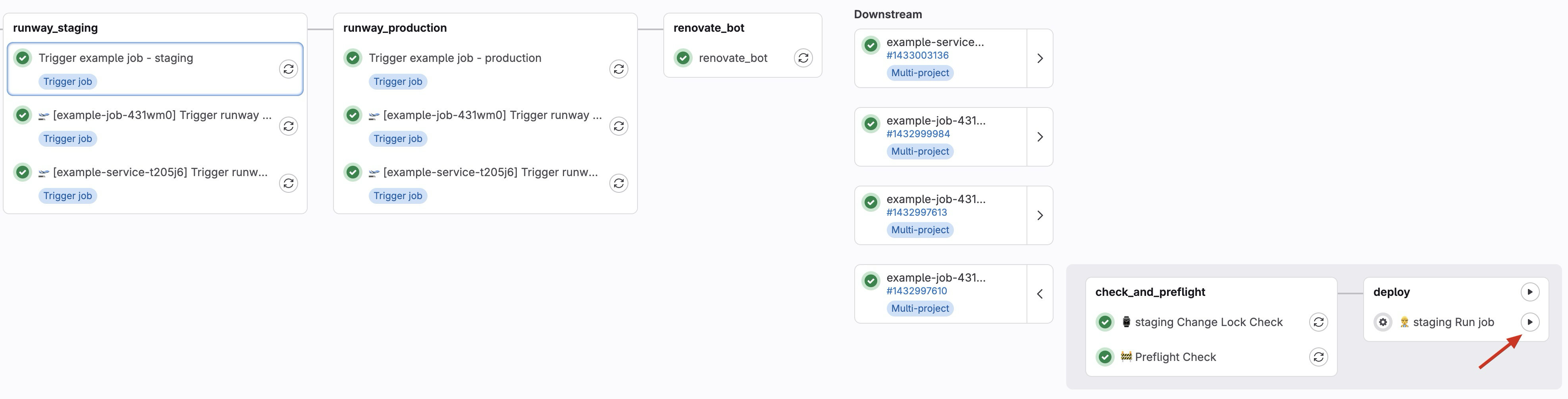
To actually trigger these jobs manually, you need to expand the downstream jobs and click on the play button:
Overriding job arguments
Section titled “Overriding job arguments”If you want to be able to trigger on-demand jobs on your Docker image with
different arguments, you can make use of the RUNWAY_JOB_OVERRIDE_ARGS
variable and avoid creating a Runway service for each job that you want to
trigger with different arguments:
Instead of:
include: - project: 'gitlab-com/gl-infra/platform/runway/runwayctl' file: 'ci-tasks/service-project/runway.yml' inputs: runway_service_id: foo-db-maintenance image: "$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/app:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA}" runway_version: v3.40.0 - project: 'gitlab-com/gl-infra/platform/runway/runwayctl' file: 'ci-tasks/service-project/runway.yml' inputs: runway_service_id: foo-user-maintenance image: "$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/app:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA}" runway_version: v3.40.0
Trigger DB Maintenance - staging: extends: .[foo-db-maintenance] Execute Job staging
Trigger User Maintenance - staging: extends: .[foo-user-maintenance] Execute Job stagingapiVersion: runway/v1kind: RunwayJobmetadata: ...spec: ... command: - my-app args: - db-maintenanceapiVersion: runway/v1kind: RunwayJobmetadata: ...spec: ... command: - my-app args: - user-maintenance… you can achieve the same thing using RUNWAY_JOB_OVERRIDE_ARGS and just one
service:
include: - project: 'gitlab-com/gl-infra/platform/runway/runwayctl' file: 'ci-tasks/service-project/runway.yml' inputs: runway_service_id: foo-maintenance image: "$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/app:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA}" runway_version: v3.40.0
Trigger DB Maintenance - staging: extends: .[foo-maintenance] Execute Job staging variables: RUNWAY_JOB_OVERRIDE_ARGS: ["db-maintenance"]
Trigger User Maintenance - staging: extends: .[foo-maintenance] Execute Job staging variables: RUNWAY_JOB_OVERRIDE_ARGS: ["user-maintenance"]apiVersion: runway/v1kind: RunwayJobmetadata: ...spec: ... command: - my-appLimitations
Section titled “Limitations”-
Jobs do not have access to network connectivity to GitLab internal-facing endpoints. For example: you cannot run a job that hits the alert manager endpoint as this is an internal-only facing endpoint.
-
By default, each task runs for a maximum of 10 minutes (configurable via
spec.timeoutin seconds), however the max value for the timeout (i.e., maximum runtime allowed) is 24 hours (86400seconds).
- Google documentation for best practices around error-handling.